Devise fiat
Crypto-monnaies
Aucun résultat pour ""
Nous n'avons rien trouvé qui corresponde à votre recherche. Réessayez avec d'autres mots-clés.
How to Stake Ethereum: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Ethereum is one of the most popular and innovative cryptocurrencies in the world. It is not only a digital currency, but also a platform for decentralized applications (DApps) that run on smart contracts. Ethereum aims to create a global, open, and permissionless network that can support a variety of use cases, such as finance, gaming, identity, supply chain, and more.
However, Ethereum is also undergoing a major transformation, as it shifts from its current proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a proof-of-stake (PoS) one. This change will have significant implications for the security, scalability, sustainability, and economics of the network. It will also introduce new opportunities for users to participate in securing the network and earning rewards by staking their ETH.
In this article, we will explain what staking is, why it is important for Ethereum, how it works, and how you can stake your ETH using different methods. We will also cover some of the benefits and risks of staking, as well as some tips for finding a trustworthy staking platform.
What is Staking?
Staking is the act of depositing ETH to activate validator software that helps secure the network and process transactions. As a validator, you will be responsible for storing data, processing transactions, and adding new blocks to the blockchain. This will keep Ethereum secure for everyone and earn you new ETH in the process.
Staking is part of Ethereum's transition to PoS, which is expected to be completed by late 2022 or early 2023. PoS is a consensus mechanism that allows the network to reach agreement on the state of the blockchain without relying on expensive and energy-intensive PoW computations. Instead, PoS relies on validators who stake their ETH as a form of collateral and incentive to behave honestly and follow the rules of the protocol.
Staking is a public good for the Ethereum ecosystem, as it improves the security, scalability, and sustainability of the network. It also allows anyone with any amount of ETH to help secure the network and earn rewards in the process.
Why Stake Your ETH?
There are several reasons why you might want to stake your ETH:
- Earn rewards: Staking ETH allows you to earn passive income by receiving rewards for your contribution to the network. The rewards are given for actions that help the network reach consensus, such as proposing and attesting new blocks. The current annual percentage rate (APR) for staking ETH is around 5%, but this may vary depending on the number of validators and the amount of ETH staked in the network.
- Support security: Staking ETH helps secure the network against attacks, as it makes it more costly and difficult for malicious actors to control a majority of validators. To become a threat, an attacker would need to hold at least 51% of the validators, which means they would need to control at least 51% of the ETH staked in the system. This would be very expensive and risky, as they would also lose their stake if they are caught violating the protocol rules.
- Enhance sustainability: Staking ETH reduces the environmental impact of Ethereum, as it eliminates the need for PoW computations that consume a lot of electricity and generate a lot of heat and emissions. Staking nodes can run on relatively modest hardware using very little energy, making Ethereum more eco-friendly and accessible.
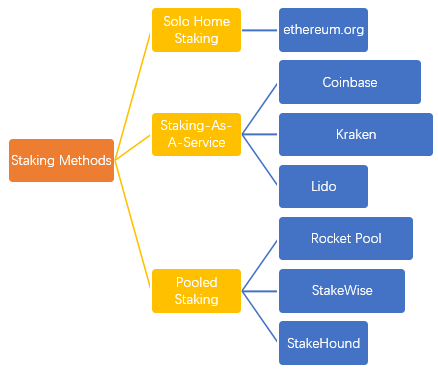
Methods for Staking ETH
There are different ways to stake your ETH depending on how much you are willing to stake and how much control you want to have over your validator node. You will need at least 32 ETH to run your own validator node, but you can also stake less by using other options. Here are some of the most common methods for staking ETH:
- Solo home staking: This is the most decentralized and trustless way of staking ETH, as it gives you full control over your validator node and your rewards. However, it also requires more technical skills and resources, as you will need to set up and maintain your own hardware and software that runs 24/7 and stays connected to the internet. You will also need to monitor your node's performance and update it regularly according to protocol changes. If you are interested in solo home staking, you can follow this guide from ethereum.org.
- Staking-as-a-service: This is a more convenient and user-friendly way of staking ETH, as it allows you to delegate the operation of your validator node to a third-party service provider while still retaining ownership of your funds and keys. This way, you don’t have to worry about hardware or software issues or maintenance costs. However, this method also involves some trust assumptions and fees, as you will need to rely on the service provider to run your node properly and securely and to pay you your rewards. Some examples of staking-as-a-service platforms are Coinbase, Kraken, and Lido.
- Pooled staking: This is a more accessible and flexible way of staking ETH, as it allows you to stake any amount of ETH without having to run your own node or use a third-party service. Instead, you can join a pool of other stakers who collectively run a validator node and share the rewards proportionally. This way, you can benefit from the economies of scale and the expertise of the pool operator. However, this method also involves some trade-offs and risks, such as lower rewards, higher fees, liquidity issues, and smart contract vulnerabilities. Some examples of pooled staking platforms are Rocket Pool, StakeWise, and StakeHound.
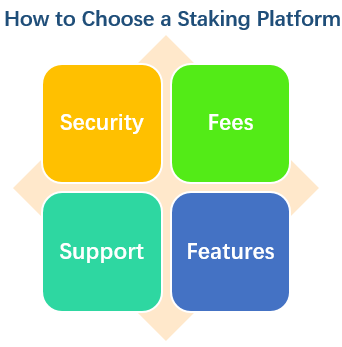
How to Choose a Staking Platform
If you decide to use a staking-as-a-service or a pooled staking platform, you will need to do some research and due diligence before choosing one. There are many factors to consider when evaluating a staking platform, such as:
- Security: The platform should have a proven track record of securing its users’ funds and data, as well as complying with the protocol rules and standards. It should also have adequate security measures in place, such as encryption, backups, audits, insurance, etc.
- Fees: The platform should have a transparent and reasonable fee structure that reflects the value and quality of its service. It should also disclose any hidden or variable fees that may affect your returns.
- Reputation: The platform should have a good reputation in the Ethereum community and among its users. It should also have positive reviews and ratings from reputable sources and platforms.
- Support: The platform should have a responsive and helpful customer support team that can assist you with any issues or questions you may have. It should also have clear and comprehensive documentation and guides that can help you understand how the platform works and how to use it effectively.
- Features: The platform should have features that suit your needs and preferences, such as user interface, dashboard, analytics, notifications, etc. It should also have features that enhance your staking experience, such as flexibility, liquidity, automation, etc.
How to Stake ETH: A Step by Step Guide
Staking ETH is not a complicated process, but it does require some preparation and attention. Here are the steps you need to follow to stake your ETH successfully:
Step 1: Choose a Staking Method
The first step is to decide how you want to stake your ETH. As we mentioned before, there are different methods available, each with its own pros and cons. You should choose the one that suits your budget, skills, and preferences.
- If you have at least 32 ETH and want to have full control and responsibility over your validator node, you can opt for solo home staking. This is the most decentralized and trustless way of staking, but it also requires more technical knowledge and resources. You will need to set up and maintain your own hardware and software that runs 24/7 and stays connected to the internet. You will also need to monitor your node's performance and update it regularly according to protocol changes.
- If you have at least 32 ETH but don't want to deal with hardware or software issues, you can opt for staking-as-a-service. This is a more convenient and user-friendly way of staking, but it also involves some trust assumptions and fees. You will need to delegate the operation of your validator node to a third-party service provider while still retaining ownership of your funds and keys. The service provider will run your node on your behalf and pay you your rewards.
- If you have less than 32 ETH or want more flexibility and accessibility, you can opt for pooled staking. This is a more accessible and flexible way of staking, but it also involves some trade-offs and risks. You will need to join a pool of other stakers who collectively run a validator node and share the rewards proportionally. The pool operator will handle the technical aspects of running the node and charge you a fee for their service.
Step 2: Choose a Staking Platform
The next step is to choose a staking platform that offers the staking method you prefer. There are many platforms available, each with its own features, fees, reputation, and support. You should do some research and due diligence before choosing one, as we explained in the previous section.
Some examples of staking platforms are:
- For solo home staking: ethereum.org
- For staking-as-a-service: Coinbase, Kraken, Lido
- For pooled staking: Rocket Pool, StakeWise, StakeHound
You can also use this list of verified staking providers from ethereum.org as a reference.
Step 3: Prepare Your ETH
The third step is to prepare your ETH for staking. Depending on the staking method and platform you choose, this may involve different steps.
- For solo home staking: You will need to generate a set of validator credentials using the official Ethereum launchpad or another tool recommended by ethereum.org. These credentials include two pairs of keys: one for signing blocks (signing key) and one for withdrawing funds (withdrawal key). You will need to keep these keys safe and secure, as they are essential for running your validator node and accessing your funds. You will also need to deposit 32 ETH per validator from an Ethereum 1 wallet (such as MetaMask) to the official deposit contract using the launchpad or another tool. This will activate your validator node on the Ethereum 2 network.
- For staking-as-a-service: You will need to follow the instructions provided by the service provider to create a set of validator credentials, upload your signing keys to them, and deposit 32 ETH per validator from an Ethereum 1 wallet (such as MetaMask) to their platform or directly to the deposit contract. This will allow the service provider to run your validator node on your behalf and pay you your rewards.
- For pooled staking: You will need to follow the instructions provided by the pool operator to connect your Ethereum 1 wallet (such as MetaMask) to their platform and deposit any amount of ETH you want to stake. This will allow the pool operator to run a validator node on behalf of all the pool members and distribute the rewards proportionally.
Step 4: Start Staking and Earning Rewards
The final step is to start staking and earning rewards. Once you have deposited your ETH and activated your validator node (or delegated it to someone else), you will start receiving rewards periodically for helping secure the network.
The rewards are calculated based on several factors, such as:
- The amount of ETH you stake
- The number of validators in the network
- The performance of your validator node
- The fees charged by the platform or pool operator
You can use this calculator from ethereum.org to estimate your potential rewards based on different scenarios.
Conclusion
Staking ETH is a rewarding and exciting way to support the Ethereum network and its transition to PoS. However, it also requires some preparation and attention, as well as some risks and trade-offs. You should do your own research and due diligence before choosing a staking method or platform, and be prepared to monitor your staking performance and adjust your strategy accordingly. Staking ETH is not a get-rich-quick scheme, but rather a long-term commitment that requires patience and responsibility.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to contact me. I hope you enjoyed this article and learned something new. Happy staking!
Stay tuned to CoinCarp Social Media and Discuss with Us:
Up to $6,045 Bonuses
Sponsored
Join Bybit and receive up to $6,045 in Bonuses! Register Now!