フィアット通貨
仮想通貨
How to Protect Your DeFi Assets from Flash Loan Attacks?
Flash loan attacks are a new form of cybercrime that targets decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. In this article, we will explore what flash loan attacks are, how they operate, why they are so prevalent in DeFi, and how to prevent them.
What Is a Flash Loan Attack?
A flash loan attack is a malicious exploit that uses flash loans, which are uncollateralized loans that must be repaid within one blockchain transaction. Flash loans are a novel feature of DeFi that allow users to borrow large amounts of crypto assets without any collateral or credit checks. Flash loans are useful for legitimate purposes such as arbitrage trading or refinancing debt. However, they also enable hackers to manipulate the market and steal funds from other users or protocols.
A flash loan attack typically involves the following steps:
- The hacker borrows a huge amount of crypto assets from a DeFi lending platform using a flash loan.
- The hacker uses the borrowed assets to manipulate the price of a target asset on one exchange or protocol.
- The hacker exploits the price discrepancy to siphon funds from another exchange or protocol that depends on the manipulated price data.
- The hacker repays the flash loan with a small interest and keeps the rest of the stolen funds as profit.
The key to a successful flash loan attack is to repay the loan within the same transaction block. This allows the hacker to access massive liquidity without any collateral, making it hard for lending platforms to defend against these attacks.
How Flash Loan Attacks Work?
A flash loan attack can vary depending on the specific protocols involved and the type of manipulation used by the hacker. However, some common types of manipulation include:
- Oracle manipulation: An oracle is a service that provides external data to smart contracts, such as price feeds. Some DeFi protocols use oracles to determine the value of their assets or collateral. A hacker can use a flash loan to artificially inflate or deflate the price of an asset on one exchange that is used by an oracle, and then use that false price data to exploit another protocol that relies on that oracle.
- Liquidity pool manipulation: A liquidity pool is a pool of funds that provide liquidity for trading on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap or Sushiswap. Users can deposit their crypto assets into liquidity pools and earn fees from each trade. However, liquidity pools are also vulnerable to flash loan attacks because they use an algorithm to determine the price of each asset based on its supply and demand in the pool. A hacker can use a flash loan to skew the balance of a liquidity pool and create an artificial price difference between two assets, and then exploit that difference to drain funds from another protocol that uses the same liquidity pool.
- Reentrancy attack: A reentrancy attack is a type of smart contract vulnerability where a hacker can repeatedly call a function within a single transaction and execute malicious code before the original function is completed. This allows the hacker to withdraw more funds than they should be able to. A hacker can use a flash loan to initiate a reentrancy attack on a protocol that has this vulnerability and steal funds from it.
Flash Loan Attack Case Studies
Flash loan attacks have been making headlines since DeFi’s popularity boom in 2020 and appear to be increasing in frequency and severity in 2021, causing hundreds of millions of dollars in losses so far. Here are some examples of flash loan attacks that have happened in the past:
- PancakeBunny Attack: In April 2022, PancakeBunny, a yield farming protocol on Binance Smart Chain (BSC), was attacked for over $200 million. The hacker borrowed 700,000 BUNNY and 114,000 BNB tokens from PancakeSwap, another DEX on BSC, and used them to manipulate the price of BUNNY on PancakeSwap. The hacker then exploited the inflated price of BUNNY to mint new BUNNY tokens from PancakeBunny and dumped them on the market, crashing the price of BUNNY by 75%.
- DeFi Yield Farming Aggregator ApeRocket Flash Loan Attack: In May 2021, ApeRocket, a DeFi yield farming aggregator on BSC, was attacked for $1.26 million. The hacker used a flash loan of 19 million BNB tokens from PancakeSwap and manipulated the price of ApeRocket’s native token SPACE on PancakeSwap. The hacker then exploited the inflated price of SPACE to withdraw more funds than they should from ApeRocket’s liquidity pools.
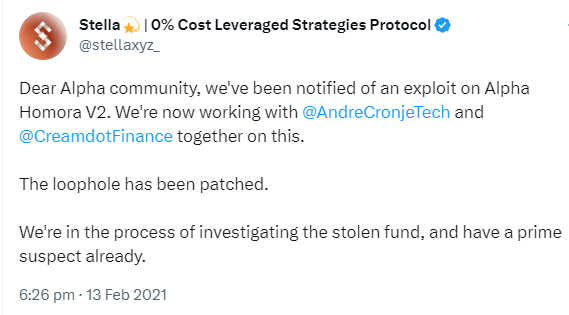
- Alpha Homora Protocol Hack: In February 2021, Alpha Homora, a leveraged yield farming protocol on Ethereum, was hacked for $37 million. The hacker used a flash loan of 13,000 ETH from Aave and exploited a reentrancy vulnerability in Alpha Homora’s smart contract. The hacker was able to repeatedly withdraw funds from Alpha Homora’s lending pool without updating their debt balance, effectively draining the pool.
Why Flash Loan Attacks Are Common in DeFi
Flash loan attacks are the most common types of DeFi attacks because they are cheap and low-risk for the hackers. There are two main reasons why flash loan attacks are so widespread in DeFi:
- Flash Loan Attacks Are Cheap: Flash loan attacks do not require any upfront capital or collateral from the hacker. The hacker only needs to pay a small fee to the lending platform that provides the flash loan, which is usually a fraction of a percent of the borrowed amount. This means that anyone with some technical skills and a small amount of funds can execute a flash loan attack.
- Flash Loan Attacks Are Low-Risk: Flash loan attacks are also very low-risk for the hacker because they do not leave any trace on the blockchain. The hacker can use various techniques to hide their identity and origin of funds, such as using multiple wallets, mixing services, or anonymous protocols. Moreover, since flash loans are executed within one transaction block, the hacker does not have to worry about market fluctuations or countermeasures from other protocols or users.
How to Prevent Flash Loan Attacks
Flash loan attacks are a serious threat to the security and stability of DeFi protocols and users. However, there are some possible ways to prevent or mitigate flash loan attacks, such as:
- Use Decentralized Oracles for Price Data: Decentralized oracles are services that provide secure and reliable data to smart contracts from multiple sources. By using decentralized oracles for price data, DeFi protocols can reduce their reliance on single exchanges or liquidity pools that can be manipulated by flash loan attackers. Some examples of decentralized oracles are Chainlink, Band Protocol, and UMA.
- Force Critical Transactions to Go Through Two Blocks: Another way to prevent flash loan attacks is to force critical transactions that involve large amounts of funds or sensitive operations to go through two blocks instead of one. This means that the transaction will not be executed until it is confirmed by another block after it is broadcasted. This can increase the security of the transaction by making it harder for flash loan attackers to manipulate the market within one block.
- Use Flash Loan Attack Detection Tools: Flash loan attack detection tools are software applications that monitor the blockchain activity and alert users or protocols when a suspicious transaction involving a flash loan occurs. These tools can help users or protocols to react quickly and take appropriate actions to stop or minimize the damage caused by flash loan attacks. Some examples of flash loan attack detection tools are PeckShield, CertiK, and Rekt.
Conclusion
Flash loan attacks are a type of cybercrime that exploits the vulnerabilities of DeFi protocols using flash loans, which are uncollateralized loans that must be repaid within one transaction block. Flash loan attackers use various types of manipulation techniques to create artificial price differences between different exchanges or protocols and drain funds from them.
Flash loan attacks are common in DeFi because they are cheap and low-risk for the attackers. However, there are some possible ways to prevent or mitigate flash loan attacks, such as decentralized oracles and detection tools. Most importantly, before you invest, make sure you understand the potential losses and only use money that you can spare. The key to successful investing is to manage your risk well, and this applies to DeFi staking too.
Stay tuned to CoinCarp Social Media and Discuss with Us:
- Bybit Adds USDT0 Access to HyperEVM, Corn, and Berachain for Unified Stablecoin Transfers 初級 Aug 04, 2025 2分
- Trading with 500x+ Leverage on MEXC: What You Should Know 初級 Aug 01, 2025 5分
- Bitget Climbs to Top 3 in Global Derivatives Market, Bitcoin.com Report Finds 初級 Jul 31, 2025 2分
- Bitget Introduces Rhea Finance (RHEA): Earn Rewards via CandyBomb and Community Campaign 初級 Jul 31, 2025 2分