명목화폐
암호화폐
What Is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) are a type of cryptocurrency marketplace that connect crypto sellers and buyers directly, allows for peer-to-peer(P2P) cryptocurrency transactions online and without the need for an intermediary agency. It means you can exchange assets on DEX without having to trust your funds with another entity. These kinds of exchanges have become quite popular in recent years since they align with the fundamental philosophy of blockchain technology--Decentralization.
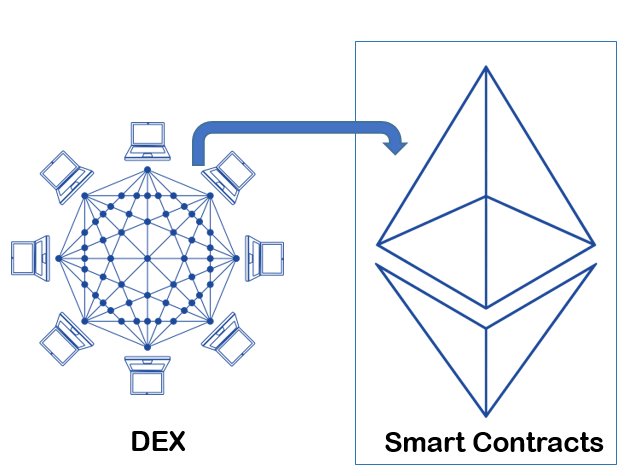
How Does a Decentralized Exchange (DEX) Work?
To realize the decentralization, third-party (e.g. banks, stockbrokers, online payment gateways, government institutions, etc.) which take custody of user funds and oversees the security and transfer of assets are replaced by a blockchain or distributed ledger. Smart contracts were used by DEXs to execute market transactions by allocating transactions' operations to autonomous code, although there are multiple variations of order fulfillment with differing degrees of decentralization. In this way, users remain in control of their private keys when transacting on a DEX platform.
How Many Types of Decentralized Exchanges?
Actually, most of the DEXs are semi-decentralized, using their own servers and off-chain order books to store data and external programs or entities for the exchange of user assets. With the degrees of decentralization, there are 3 types of decentralized exchanges.
- On-chain order books: Everything is processed on-chain including modifying and canceling orders. By placing all stages of order onto the blockchain, they go through a time-consuming process of asking every node on the network to permanently store the order via miners, as well as pay a fee.
- Off-chain order books: Off-chain orders are posted elsewhere such as a centralized entity that governs the order book. Through smart contracts, a DEX can provide a framework for parties to manage off-chain order books. Hosts can then access a larger liquidity pool and relay orders between traders. Once the parties are matched, the trade can be executed on-chain. Off-chain order books can provide faster speeds because it takes less congestion and confirmation time.
- Automated market maker (AMM): These platforms typically employ liquidity pool protocols to determine asset pricing. AMMs decentralize this process and allow users to create a market on a blockchain. No counterparty is needed to make a trade, instead of transacting directly with another person, exchange, or market-maker, users trade with smart contracts and provide liquidity.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Decentralized Exchanges?
Pros:
- Diversity: Many altcoins can be listed on DEXs, where P2P transactions can occur without high trading volumes. This provides a wider opportunity for engagement in digital assets and enhances financial inclusion.
- Privacy: Users aren't typically required to complete KYC and AML procedures when using DEXs.
- Custody: Users don't need to provide private keys.
- Lower Fees: With the use of self-executing smart contracts, DEXs charge a low fee than centralized Exchanges.
Cons:
- Liquidity: Because DEXs are still relatively new, market segregation has a negative impact on market liquidity.
- Lack of support of fiat: Lack of fiat is a barrier to entry for novice users.
- User Experience: It is more complicated to use, compare to centralized exchanges.
What Are the Differences Between Decentralized Exchanges and Centralized Exchanges?
Although these two types of cryptocurrency exchanges provide a vital source of liquidity to the global cryptocurrency market, facilitating billions of dollars in trading volume on a daily basis, decentralized exchanges operate differently from Centralized exchanges:
Decentralized Exchanges | Centralized Exchanges | |
1 | Without an intermediary organization. | With an intermediary organization. |
2 | Lower fees | Higher fees |
3 | Non-custodial framework, users hold their own private keys. | Custodial your assets |
4 | KYC is not required | Most of the centralized Exchanges require KYC |
5 | Not required to follow Anti-Money-Laundering (AML) regulatory standards | Most of the centralized Exchanges follow Anti-Money-Laundering (AML) regulatory standards |
Is Decentralized Exchange Safe?
- There are several possible risks associated with decentralized exchanges, which can be avoided to some extent on centralized exchanges. These include fake tokens with the same ticker as the real coins, high slippage that resulting in buying a token at a price different than the market's average, transaction delays, and lack of trading pair data.
- Also, because of DEXs' non-custodial framework, you will responsible for the custody of your cryptocurrency. However, this comes with the risk that your keys could get lost, stolen, or destroyed, and if no one knows your password, your will lost your assets.
- Operators of decentralized exchanges can face legal consequences from government regulators, they may face the risk of money laundering.
What Are the Top 10 Decentralized Exchanges?
Based on trading volumes, market share of DeFi markets, there are 10 well-known decentralized exchanges:
Uniswap, PancakeSwap, MDEX(BSC), MDEX, 1inch Liquidity Protocol, 1inch Liquidity Protocol, 1inch Exchange, Sushiswap, Curve Finance, QuickSwap.
에서 찾아주세요:
X (Twitter) | Telegram | Reddit
지금 CoinCarp 앱을 다운로드하세요: https://www.coincarp.com/app/
- Merging cryptocurrency with traditional investment strategies 초급 Oct 29, 2025 3분
- Reasons Behind the Rise of Crypto in Sports Betting 초급 Oct 26, 2025 3분
- Barclays Boosts Tesla Price Estimate to $350 Ahead of Q3 Results 초급 Oct 22, 2025 3분
- Gold's Historic Drop Marks a Sharp Pause in Year-Long Rally: Will It Fall Under $4,000? 초급 Oct 22, 2025 3분