명목화폐
암호화폐
"" 해당 결과 없음
검색에 일치하는 항목을 찾을 수 없습니다.다른 용어로 다시 시도하십시오.
What Is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a special type of database, which is the technological foundation behind cryptocurrencies. In essence, it is a chain of cryptographic-based blocks, and each block contains authenticated data. All the data on a blockchain is designed to be publicly accessible. Besides, the date can be added, but its virtually impossible to modify or delete once the data has been stored.
Blockchain technology first came to prominence in 2009 when Satoshi Nakamoto launched Bitcoin with inspiration from earlier technologies and proposals. Nowadays, blockchain technology is widely applied as a suite of distributed ledger technologies to record and track data, which is different from the age-old ledger method. The distributed ledger technology is protected by cryptography and maintained by a huge network of computers or nodes.
How Are Blocks Connected?
Hashing is the glue that connects the blocks. It refers to the process of generating a fixed size output from input data by using mathematical formulas. Any minor modification to the input data will produce a completely different output. Thus, hashing is unpredictable, and reverse calculation is impossible.
In fact, a block consists of a specific hash that defines itself and a partial hash of the previous block. Each block is created based on the previous block and contains a piece of information linked to the previous block. Therefore, hash connects blocks to a chain, which is called a blockchain. Each block can point back to the previous one by including its hash, and any attempt to edit older blocks will immediately become apparent.
For instance, if we have a chain of 3 blocks, assuming that the hash value of the second block is 2DEF, then the third block will contain 2DEF as part of its hash value. As a result, if a hacker tampered with the second block, it would cause the hash value of the block to change as well. At the same time, it will invalidate the second block and all subsequent blocks because they no longer have the valid hash of the previous block.
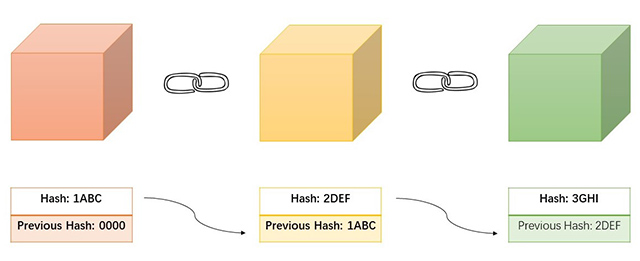
The first block cannot point to the previous block, which is known as the genesis block.
Blockchain Features
Here are three of the most distinctive features of blockchain technology:
- Decentralization
As we know, although online payment appears to be a direct transaction between the two parties, in fact, there is a third-party intermediary behind every transaction, which is usually a worthy authority such as the government and banks. In this scenario, the intermediary serves as a trading center, responsible for recording every transaction in the system and compiling the data into a ledger. However, if the intermediary is hacked and the ledger is tampered with, the entire trading system will be at risk.
Compared with storing data at a traditional trading center, blockchain technology changes the way to store and track data. Through the use of blockchain technology, transactions are conducted directly between the two parties, replacing a third-party trading center, which avoids the risk of the transactions being controlled by the centralized intermediary or the entire trading system collapse from the center.
When a transaction occurs, both parties of the transaction will publish the information on the blockchain. Subsequently, the volunteers will record this information and enter it into a ledger, and then broadcast the ledger back to the system. As a result, the ledger in the blockchain system is not controlled by a single intermediary, but by each participant in the system, which is a manifestation of decentralization. In other words, no one has the right to edit the entries outside of system rules, and the participants have the most realistic record available at any given moment.

- Trusted Data
Blockchain stores information in blocks that are linked together in a chronological fashion to form a continuous line. The data that is stored inside a block depends on the type of blockchain. For instance, the Bitcoin blockchain stores the details about a transaction, such as a sender, receiver, and amount of coins. In order to achieve significant levels of data integrity and security, blockchain adopts cryptographic hash function as the core technology to prevent data from tampering.
When a transaction is initiated, it will be sent across the blockchain network. Before creating a block to record the transaction information, a cryptographic hash must be calculated and resolved. The hash can be considered as a fingerprint that identifies a block and all of its contents, and is always unique. Changing the data within the block will cause the hash to change. In addition, the answer to the hash in each block is placed simultaneously at the beginning of the next block and becomes part of the next block. In this way, the blocks are connected to a chain. If someone wants to tamper with one of the blocks, it will change the hash value of that block, and then all subsequent blocks will be invalidated. As such, it protects the data stored on the blockchain.
In addition, a block is considered valid and added to the blockchain only when it has proof-of-work. Proof-of-work is a form of arbitrary cryptographic mathematical puzzle that needs to be solved to prove that a certain amount of specific computational work has been expended. It is a mechanism to ensure that every block added to the blockchain has the consensus of the entire network. When a node finds a proof-of-work value that can be calculated to obtain a qualified hash value, it will be broadcast to the entire network immediately, and the hash value will be confirmed and verified by the nodes in the network. This process usually takes approximately 10 minutes, which makes blocks difficult to tamper with. More specifically, proof-of-work slows down the creation of new blocks, while to tamper with the information on one block, proof-of-work on the other blocks must be completed, making it much more difficult.
As a result, the security of blockchain comes from the creative use of hashing and proof-of-work mechanisms. In order to successfully tamper with the information on the blockchain, hackers need to tamper with all blocks on the chain, redo the proof-of-work for each block, and control more than 50% of the peer-to-peer network, which is almost impossible.

- Transparent and Tracable
Instead of using a central entity to manage, blockchain adopts a peer-to-peer network in which everyone can participate directly. All participants in the network can get a full copy of the blockchain. When a new block is added to the chain, the data is propagated throughout the network so that each participant can update their own copy of the ledger. Even if someone leaves the network, the remaining users can still access the blockchain and share information with each other. Thus, blockchain ensures the transparency and traceability of the data stored on the network.
Pros and Cons of Blockchain
- Pros
- The immediate benefit of the Bitcoin blockchain is that transactions can be transmitted without involving an intermediary. The absence of intermediaries reduces the risk to users involved and results in lower fees as no intermediaries draw commissions from them.
- The public blockchain network is a permissionless environment with no barrier to entry. Everyone is able to interact with other peers as long as they are connected to the Internet.
- A high degree of security and censorship resistance. To paralyze a centralized service, hackers only need to attack one server. But in a peer-to-peer network, each node acts as its own server. For instance, a system like Bitcoin has more than 10,000 visible nodes scattered around the world, which makes it almost impossible for an attacker to disrupt the network.
- Cons
- The most obvious barrier to the adoption of blockchains is that they do not scale well, since all participants must be kept in sync, new information cannot be added too quickly in order to keep the nodes up to date. As a result, developers will intentionally limit the update speed of the blockchain to ensure that the system remains decentralized. From the user's point of view, this will indicate that it will extend the waiting time for transactions.
- Blockchain systems are not easy to upgrade. Unlike building your own software that can add new functionality at any time, it is much more difficult to make changes in an environment with potentially millions of users. Developers can change some parameters of node software, but if the modified software is not compatible with other nodes, they will recognize and refuse to interact with your nodes. The only way to drive change is for the majority of the ecosystem to accept it. For major blockchains, it may take months or even years of intensive discussion on forums before changes can be coordinated.
Blockchain Application
The role of blockchain is not limited to cryptocurrencies and digital tokens. As a secure and reliable data management system without the participation of powerful intermediaries, blockchain technology may help solve problems in many fields such as finance, property rights, public welfare, Internet of Things, and bring about tremendous changes to the whole society.
- Public and Private Blockchains
Bitcoin is a prominent example of a public blockchain. A public blockchain means that everyone is able to view and access the transactions on it, and all it takes to join is an internet connection and necessary software. Since there are no other requirements for participation, public blockchains are considered as the permissionless environment. In contrast, a private blockchain establishes rules about who can view and interact with the blockchain. Therefore, private blockchains are considered as permission environments
In addition, there is another type of blockchain called a hybrid public-private blockchain. For instance, in some cases, participants with private permissions can view all data on the blockchain, while others can only view part of the information. In other cases, everyone can see all the data, but only some authorized people can add new data.
- Blockchain Use Cases: Charity
Charitable organizations often encounter barriers to success due to a lack of transparency, accountability issues, and limits to the ways they can accept donations. The use of blockchain technology to facilitate charitable contributions, also called crypto-philanthropy, provides an alternative solution to decentralization and direct transactions that can help these organizations accept donations and raise funds more effectively.

- Cryptocurrency Donations
Currently, a small number of charitable organizations have embraced cryptocurrencies as a donation method. However, organizations that support this approach are not the mainstream. Donors who intend to use cryptocurrency may have to select a supporting organization or donate a sufficient amount to convince their favorite charity to accept crypto payments.
Before a charity organization starts accepting cryptocurrency donations, it needs to have a transparent and efficient mechanism to manage and distribute the money. Understanding the basics of blockchain technology, as well as how to convert donations into fiat currency, is critical for effective strategy implementation.
- Potential Benefits of Crypto-philanthropy
1) Total Transparency - Each cryptocurrency transaction is securely recorded and can be easily tracked through the blockchain. Higher levels of transparency and public accountability give donors confidence and strengthen the reputation of the charity's integrity.
2) Global and Decentralized - Most blockchain networks exhibit a high degree of decentralization and do not rely on the central government or other institutions. As a result, funds can be transferred directly from donors to charities, reducing the risk of funds being misappropriated. In addition, the decentralized nature of blockchain also makes it particularly suitable for international transactions, with lower fees and faster transfers.
3) Digital Agreement - Crypto-philanthropy can be used to ensure that important documents or contracts cannot be modified without the approval of all relevant members, as blockchain is a non-destructive way to track data changes over time.
4) Reduced Expenses - Blockchain technology has the potential to simplify the way charities are managed, automate some processes and reduce overall costs through the elimination of intermediaries.
- Concerns and Limitations
1) Volatility - Most cryptocurrencies are traded in highly volatile markets, with their value often fluctuating sharply.
2) Security - If the private keys used to donate funds are lost, there is no way to retrieve them. Similarly, if the keys are not properly managed and protected, the funds in the wallet may be stolen.
3) Public Awareness and Understanding - Numbers of potential donors do not trust the blockchain system or use it for charitable donations, due to their lack of understanding of the blockchain system.
- Real-World Cases
In recent years, crypto-philanthropy has been embraced by a number of well-known charitable organizations. For instance, Fidelity Charitable, a global charity organization, received the equivalent of $69 million in cryptocurrency donations in 2017. In the same year, an anonymous donor named Pine distributed approximately $55 million in Bitcoin donations to organizations around the world through the Pineapple Fund. Moreover, the Blockchain Charity Foundation (BCF) is another notable example of crypto-philanthropy. The BCF is a non-profit organization that aims to transform philanthropy through the use of decentralized blockchain technology.
에서 찾아주세요:
X (Twitter) | Telegram | Reddit
지금 CoinCarp 앱을 다운로드하세요: https://www.coincarp.com/app/
Up to $6,045 Bonuses
Sponsored
Join Bybit and receive up to $6,045 in Bonuses! Register Now!