Fiat currencies
Crypto Currencies
No results for ""
We couldn't find anything matching your search.Try again with a different term.
What Is The Difference Between ICO, STO, IEO, IDO?
Introduction
If a company wants to raise money to develop new products or expand its business, it has a number of options. The traditional options are to seek a financial loan or an investment from a bank or venture capital. However, with the success of cryptocurrencies, more and more companies are turning to them as a way to raise money through token sales. The company will create cryptocurrencies and issue them to the public in exchange for other major cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies. This process is called raising money by issuing tokens. There are different methods of doing token sales, namely ICOs, STOs or IEOs, and the latest method is the Initial Dex Offering.

What Is Initial Coin Offering (ICO)?
ICO stands for Initial Coin Offering and is a method for teams to raise funds for projects in the cryptocurrency field. It refers to a team generating blockchain-based tokens to fund for its operation by selling the tokens directly to investors at a discount. This term comes from the traditional financial term, Initial Public Offering (IPO), which refers to the sale of stock by a company in order to raise money from the public. However, the two are fundamentally different methods of acquiring funding.

An IPO is usually for those mature companies that raise funds by selling part of the company's equity. ICOs, by contrast, are used as a funding mechanism that allows companies to raise money for their projects at a very early stage, even when the product has not yet officially launched, and are suitable for tech startups. When ICO investors buy the tokens, they are not buying any ownership in the company. The general idea is that if investors believe that the project is valuable, they will purchase the tokens that can power the project at a lower price beforehand, and then sell these tokens at a profit after the project is successful.
ICO was popularized in 2014 for being used to fund the development of Ethereum. In mid-2014, one Ether token (ETH) sold for about $40 cents. If you bought Ether tokens worth $100 in 2014, you will get the equivalent of $75,000 in 2017.
However, ICOs also contain significant risks. For instance, the decentralized autonomous organization project DAO successfully raised $150 million worth of funding on the Ethereum blockchain. However, shortly after the ICO ended, a hacker managed to steal one-third of the funds raised due to a loophole in the Ethereum code. In addition, many people today invest in ICOs not because they believe in the project, but because they just want to make quick profits. As a result, some projects continue to create hype before launching, inciting more and more people to invest in the project. But as the craze subsided, project developers and early investors began selling tokens in large numbers, which could lead to a sharp drop in prices. In addition, unlike an Initial Public Offering (IPO) that requires compliance with a large number of regulations, ICO does not need to go through these cumbersome procedures. As a result, the low barriers to entry have brought a large number of low-quality projects, some may be due to the developers, lack of the skills needed to execute the project, and some may be a simple scam from the beginning. Scammers can obtain large amounts of funds without any legal risk or public liability.
Therefore, due to the irreversibility and unregulated nature of ICOs, you should pay attention to the following when investing in ICOs:
- You need to read the ICO whitepaper to understand what you are investing in, research the project and participate in the community around it.
- Understand how tokens for a project are allocated to avoid most tokens being held by people who might sell tokens after the ICO ends to make a quick profit.
- Note if the project is overfunded. Obtaining more funds needed can lead to less efficiency, which can hinder project development.
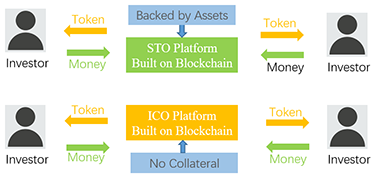
What Is Security Token Offering (STO)?
In line with the purpose of ICOs, STOs are also used as a way for companies to raise funds for their projects. In order to understand the difference between these two approaches, the fundraising tokens issued by them should be classified. Tokens can generally be divided into two categories, utility, and security. Utility tokens promise the future use of a particular product or service that has no other values, while security tokens represent tradable financial assets and promise profit.
In the case of ICOs, the lack of regulation, which has led to a large number of scams and manipulations, has drawn the attention of relevant regulators, leading them to crack down on companies conducting ICOs. Regulators want to investigate whether the tokens should in fact be treated as securities and subject to regulation. In order to avoid supervision, most ICOs classify their tokens as utility tokens when they are reviewed by authorities. As the situation got out of control, the public gradually lost their trust in ICOs. Companies such as Google and Facebook banned all ICO projects from advertising on their platforms, regulators began to intervene. Nowadays, due to concerns about regulators, most ICOs are not open to the public but are privately funded by a small number of investors.
An ICO is a completely unregulated form of raising money from around the world that is fast, easy to execute, and full of scams and frauds. On the other hand, an IPO is a long, expensive and exhausting road for legitimate companies to raise money from investors. As a result, a new type of offering called a Security Token Offering (STO) has been developed, which is in the middle ground between ICOs and IPOs. It refers to the process of selling security tokens to the public while avoiding the lengthy exhaustion process of IPOs and the lack of regulation of ICOs. STO does not offer utility tokens and is intended to comply with anti-money laundering requirements and securities laws. In short, an STO is a regulated ICO. Here are some of the benefits of STOs:
- The intrinsic value of security tokens that can be sold in the market without being tied to the issuer
- Since STOs are registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the regulation of STOs reduces investor concerns about fraud and scam
- More transparent, STO companies registered with the SEC need to disclose information including asset status, management structure, financial performance, and investor risk. In this way, investors will be able to conduct their own investigations to verify the professionalism, efficiency, and fairness of the issuing company.
- More liquidity as any asset can be tokenized
- Companies conducting STOs were given access to the global market without any conditions attached. Since digital securities can be easily marketed and transferred across borders, they can reach a broader audience of investors
- Blockchain technology improves efficiency by eliminating much of the paperwork and inefficiencies of the investment market
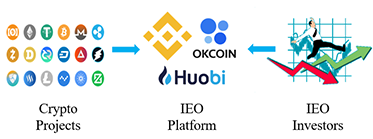
What Is Initial Exchange Offering (IEO)?
IEO stands for Initial Exchange Offering, which involves the use of a centralized cryptocurrency exchange to raise funds for a new project. With the purpose of ICOs, IEOs are managed by a cryptocurrency exchange instead of selling tokens directly to the public, and the token sale is conducted through the exchange. An IEO is often conducted when a project wants to launch its cryptocurrency or blockchain product but requires significant investment capital. With an IEO, projects can raise funds with the help of the exchange's customer base and launch trading for their tokens shortly after. The exchange facilitating the token sale and takes some responsibility for making the IEO succeed by taking care of the various aspects such as marketing, securing funds, and vetting investors. In return, the company pays a listing fee and gives some of its tokens to the exchange.
The following are several advantages of IEOs over ICOs and STOs:
- Increased trust - Since an IEO listing would have an impact on the exchange's reputation, the exchange would have the incentive to conduct extensive due diligence on each project it wants to list, meaning that suspicious projects or fraud are much less likely to occur
- Token Liquidity - Once the IEO ends, people can immediately start trading their tokens on an exchange, eliminating the situation where investors can't find a market to trade newly received tokens
- Market Advantage -- Exchanges can offer IEO to existing users, eliminating the need for companies issuing tokens to build a list of potential users from scratch
In fact, IEO's aim is to achieve a triple win for exchanges, investors and companies. With IEO, all parties can focus on achieving their specific goals. The exchange is responsible for regulatory and fund management issues, the company can focus on building its own products, and investors can understand the basic information of each project and invest with confidence
However, IEOs also have some disadvantages that mainly for companies issuing tokens:
- An IEO is expensive for some companies, even though it is an investment for marketing, security and regulation efforts
- An IEO is limited to the exchange users, which means if the exchange is not available in a specific country, those potential investors are automatically excluded from the IEO.
What Is Initial DEX Offering (IDO)?
IDO is the abbreviation of Initial DEX Offering, which is a new financing model that issues tokens through a decentralized exchange. IDO is the successor of ICO, STO, and IEO, combining the characteristics of ICO and IEO model.
First of all, the ICO is priced first and then released. In other words, first raise funds from the public and then develop products and services. However, products and services will be created in the future, which is beyond control. Therefore, there is a potential risk that the project cannot be delivered with good quality. In addition, this funding model can easily be used for financial fraud.
In contrast to the ICO model, IDO's model of issuing tokens is to circulate first and then price. The first is to establish a community, confirm membership, and release economic operation mechanisms. But the token was not priced before. Pricing in the secondary market is based on the operational effects and quality of the project. Because the IDO model does not raise funds from the public, there is no possibility of financial fraud, and its purpose is to build a network with common values. IDO avoids the legal risks of user financing and effectively solves the high-risk problem of individual investors. However, only high-quality projects can be started in IDO mode. Investors contribute to the IDO community to obtain tokens based on their own preferences and recognition of the community.
The full list of IDO platforms can be found on CoinCarp Launchpad Aggregator.
Stay tuned to CoinCarp Social Media and Discuss with Us:
X (Twitter) | Telegram | Discord | Reddit
Download CoinCarp App Now: https://www.coincarp.com/app/
Up to $6,045 Bonuses
Sponsored
Join Bybit and receive up to $6,045 in Bonuses! Register Now!