Devise fiat
Crypto-monnaies
Aucun résultat pour ""
Nous n'avons rien trouvé qui corresponde à votre recherche. Réessayez avec d'autres mots-clés.
What is Market Capitalization in Cryptocurrency?
Market capitalization, or market cap for short, is a common metric used to measure the size and value of a company, a stock, or an asset. In the context of cryptocurrency, market cap refers to the total value of all the coins or tokens that have been issued or mined in a particular blockchain network. It is calculated by multiplying the current price of one coin or token by the total number of coins or tokens in circulation.
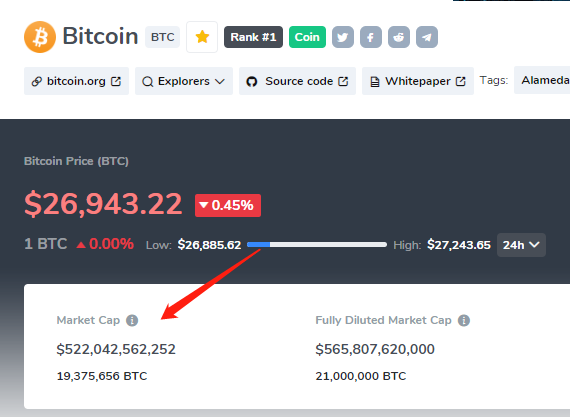
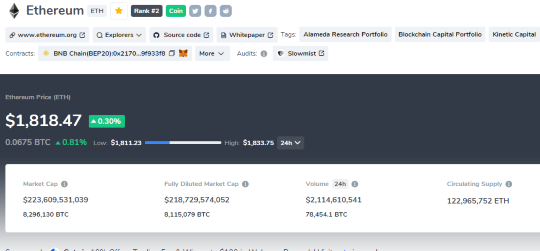
For example, as of May 17, 2023, Bitcoin has a market cap of $522.04billion, which means that there are 19.375 million bitcoins in circulation and each bitcoin is worth $26,943. Similarly, Ethereum has a market cap of $219.33 billion, which means that there are 120.287 million ethers in circulation and each ether is worth $1,823.40.
Market cap is often used as an indicator of the popularity, dominance, and growth potential of a cryptocurrency. It can also be used to compare different cryptocurrencies and evaluate their relative strengths and weaknesses. However, market cap is not a perfect measure and it has some limitations and challenges that need to be considered.
Limitations and Challenges of Market Cap
One of the main limitations of market cap is that it does not reflect the actual liquidity or trading volume of a cryptocurrency. Liquidity refers to how easily and quickly a cryptocurrency can be bought or sold without affecting its price. Trading volume refers to how much of a cryptocurrency is traded in a given period of time. Both liquidity and trading volume are important factors that affect the supply and demand of a cryptocurrency and its price movements.
For example, according to CoinCarp.com, Tether (USDT) is a stablecoin that is pegged to the US dollar and has a market cap of $83.11 billion, which makes it the third-largest cryptocurrency by market cap. However, Tether has a very high trading volume and liquidity because it is widely used as a medium of exchange and a store of value in the crypto market. On the other hand, Bitcoin SV (BSV) is a fork of Bitcoin that has a market cap of $643million, which makes it the 67th-largest cryptocurrency by market cap. However, Bitcoin SV has a very low trading volume and liquidity because it has limited adoption and support in the crypto community.
Another limitation of market cap is that it does not account for the distribution or concentration of ownership of a cryptocurrency. Distribution refers to how evenly or unevenly the coins or tokens are held by different users or entities. Concentration refers to how much of the total supply is controlled by a few large holders or whales. Both distribution and concentration can affect the stability, security, and decentralization of a cryptocurrency.
For example, Cardano (ADA) is a smart contract platform that has a market cap of $12.87 billion, which makes it the seventh-largest cryptocurrency by market cap. However, Cardano has a very uneven distribution and high concentration of ownership because about 71% of its total supply is staked by its holders, which means that they lock up their coins in exchange for rewards and voting rights. On the other hand, Dogecoin (DOGE) is a meme-based cryptocurrency that has a market cap of $10.13 billion, which makes it the nineth-largest cryptocurrency by market cap. However, Dogecoin has a very even distribution and low concentration of ownership because about 94% of its total supply is held by more than 10 million addresses, which means that it has a large and diverse user base.
A third limitation of market cap is that it does not reflect the quality or utility of a cryptocurrency. Quality refers to how well-designed, innovative, and secure a cryptocurrency is. Utility refers to how useful, functional, and valuable a cryptocurrency is for its users and applications. Both quality and utility can affect the adoption, growth, and sustainability of a cryptocurrency.
For example, Solana (SOL) is a high-performance blockchain platform that has a market cap of $8.19 billion, which makes it the eleventh-largest cryptocurrency by market cap. However, Solana has a very high quality and utility because it can process more than 50,000 transactions per second with low fees and high security, which means that it can support various scalable and efficient applications such as decentralized exchanges, gaming, and NFTs. On the other hand, Shiba Inu (SHIB) is an ERC-20 token that has a market cap of $5.17 billion, which makes it the seventeenth-largest cryptocurrency by market cap. However, Shiba Inu has a very low quality and utility because it has no clear use case or value proposition other than being a speculative asset that mimics Dogecoin's popularity.
What is the Difference Between Market Cap and Circulating Supply?
As we have seen above, market cap is calculated by multiplying the current price of one coin or token by the total number of coins or tokens in circulation. However, what exactly does circulation mean? How do we determine how many coins or tokens are available for trading? This is where circulating supply comes in.
Circulating supply is the best approximation of the number of coins or tokens that are circulating in the market and in the general public's hands. It excludes coins or tokens that are locked, reserved, burned, or otherwise not able to be sold on the public market. For example, some cryptocurrencies have pre-mined coins or tokens that are held by their founders or developers for future use or distribution. These coins or tokens are not part of the circulating supply because they are not accessible to buyers or sellers.
The circulating supply matters because it suggests how scarce a particular asset is. The more scarce an asset is, the more valuable it tends to be. This is why some cryptocurrencies have mechanisms to limit their maximum supply or reduce their inflation rate over time. For example, Bitcoin has a hard-coded limit of 21 million bitcoins that can ever be created. This means that as more bitcoins are mined over time, fewer bitcoins will be available for mining until eventually no more bitcoins can be created. This creates an artificial scarcity that increases Bitcoin's value.
However, not all cryptocurrencies have fixed maximum supplies or predictable inflation rates. Some cryptocurrencies have dynamic supplies that depend on various factors such as user behavior, network activity, governance decisions, or algorithmic adjustments. For example, Ethereum does not have a hard limit on its total supply but instead adjusts its issuance rate based on network demand and security needs. This means that Ethereum's supply can increase or decrease over time depending on various factors.
Therefore, when comparing different cryptocurrencies based on their market caps, we need to consider their circulating supplies as well as their prices. A cryptocurrency with a higher price but lower circulating supply may have a lower market cap than another cryptocurrency with a lower price but higher circulating supply.
How do I Calculate Market Capitalization for a Cryptocurrency?
To calculate market capitalization for any cryptocurrency you need two pieces of information: its current price per coin or token and its circulating supply.
The current price per coin or token can be found on CoinCarp.com. CoinCarp aggregate data from multiple sources such as exchanges , brokers , wallets , etc., to provide an average price for each cryptocurrency based on its trading volume , liquidity , demand , etc. The circulating supply can also be found on CoinCarp.
Once you have these two pieces of information you can simply multiply them together to get the market capitalization for any cryptocurrency:
Market Cap = Price x Circulating Supply
For example:
- Bitcoin: Price = $27,008.58 , Circulating Supply = 19.375 million, Market Cap = $27,008.58 x 19.375 million = $523.30 billion
- Ethereum: Price = $1,823.40 , Circulating Supply = 120.287 million, Market Cap = $1,823.40 x 120.287 million = $219.33 billion
- Tether: Price = $1 , Circulating Supply = 82.822 billion, Market Cap = $1 x 82.822 billion = $82.84 billion
Conclusion
Market capitalization is an important metric that can help us understand the size and value of different cryptocurrencies. However, it is not enough to rely on market cap alone when evaluating or comparing cryptocurrencies. We also need to consider other factors such as liquidit, trading volume, distribution, concentration, quality, and utility that can affect the performance and potential of cryptocurrencies.
Stay tuned to CoinCarp Social Media and Discuss with Us:
Up to $6,045 Bonuses
Sponsored
Join Bybit and receive up to $6,045 in Bonuses! Register Now!