명목화폐
암호화폐
"" 해당 결과 없음
검색에 일치하는 항목을 찾을 수 없습니다.다른 용어로 다시 시도하십시오.
What Is a Layer 0 Blockchain?
We have introduced the Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchain(What Is Layer 1 vs Layer 2 in Blockchain?), and both are part of the blockchain ecosystem. Apart from Layer 1 and Layer 2, you may want to know Layer 0, the foundational layer of all blockchain protocols, providing a seamless connection between them and allowing for the creation of interconnected value chains. This article will try to explain the Layer 0 Blockchain and compare it with Layer 1.
What Is Layer 0 in Crypto?
Layer 0 protocols are the basis for Layer 1 blockchains and are seen as the answer to some of the issues that the blockchain industry is facing, such as scalability and interoperability. These protocols provide a strong foundation for blockchain networks and applications.
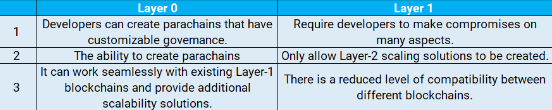
Project developers often have to make difficult design compromises when using Layer-1 blockchain protocols, as they are designed to fit the average use case. Additionally, developers are limited in their ability to make further changes unless the underlying protocol is updated. Layer-0 blockchain protocols offer a solution to these issues, enabling developers to create custom blockchains that fit their specific needs. By combining different elements from different layer-1 protocols, developers can create their own ecosystems and make performance improvements. It offers significant versatility, as they are compatible with both layer-1 blockchain solutions and more specialized layer-2 scaling solutions. They also provide developers with the tools they need to create blockchains that enable high levels of cross-chain interoperability and facilitate rapid communication between different chains.
What are the Features of Layer 0?
- Interoperability. Layer 0 protocols allow blockchain networks built on the same protocol to interact with each other without the use of dedicated bridges. By utilizing different versions of cross-chain transfer protocols, Layer 0 can be utilized to leverage the features and use cases of one blockchain's ecosystem onto another, leading to faster transactions and improved efficiency.
- Scalability. A Layer 0 infrastructure can help address the scalability issues of a monolithic blockchain such as Ethereum by allowing the critical functions of transaction execution, consensus, and data availability to be delegated to different blockchains. This means that each blockchain network built on the same Layer 0 infrastructure can be optimized to perform certain tasks more efficiently, resulting in improved scalability. For instance, execution chains can be optimized to process a high number of transactions per second.
- Flexibility. Layer 0 protocols provide developers with software development kits (SDKs) and a seamless interface to make it easy for them to create their own purpose-specific blockchains. These protocols give developers the flexibility to customize their own blockchains and determine their own token issuance models and the type of DApps they want to build on their blockchains. This encourages developers to build on these protocols

How Does Layer 0 Blockchain Work?
Layer 0 of the blockchain protocol is composed of a number of state channels that validate data through user-defined functions. This layer involves nodes, servers, systems, and any device that is connected to the nodes. It supports various consensus algorithms, and P2P systems, such as proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, proof-of-activity, proof-of-reputable observations, and directed acyclic graphs (DAG) to optimize the network topology.
If you wish to build a business using the Layer 0 protocol, you must stake or purchase the platform's native token. This token serves as the core consensus layer, providing economic incentives to encourage users to contribute to and maintain the HGTP network's ecosystem. By possessing the necessary tokens within the blockchain network, you can gain full access to the Layer 0 ecosystem, data-rich solutions, advanced solutions, and products. With these tokens, you can create your own unique tokens, construct business logic, establish reward structures, validate data, and more, all while receiving equal rewards for your efforts and forming a mutually beneficial relationship.
What are the Differences Between Blockchain Layer 0 and Layer 1?
Layer 0 is the most basic architecture, which acts as the foundation for Layer 1 chains and communication between them. Layer 1 chains are responsible for defining protocols and standards, as well as for supporting decentralized applications. These usually have their own ecosystems and structures, and the participants in the network verify transactions.
Layer 0 vs. Layer 1
What are the Layer 0 Examples?
Using an example is probably the easiest way to understand complicated technology. We will list 3 examples of Layer 0 adoptions as follows:
Polkadot is a widely-recognized Layer 0 project, and the main chain they built is called the Relay Chain. It serves as a communication bridge between different Layer 1 chains, which are known as Parachains because they exist in parallel to the Relay Chain. Two of the prominent projects building Layer 1 chains on top of Polkadot’s Relay Chain are Moonriver and Karura.
Cosmos is a foundational Layer 0 technology that enables the connection of various blockchains into a meta-blockchain system. Through this, smart contracts on one network can execute transactions on another. This interconnectivity is the core of Cosmos, and it also provides a framework for building blockchain networks, allowing interoperability with other Proof-of-Stake (PoS) networks. The Cosmos Hub, its own PoS network, records the states of other networks.
The Avalanche network is built on a tri-blockchain infrastructure, composed of the Contract Chain (C-chain), the Exchange Chain (X-chain), and the Platform Chain (P-chain). Each chain is designed to perform specific functions within the ecosystem, ensuring both security and optimal performance with low latency and high throughput. The X-Chain allows users to create and trade assets, the C-Chain to construct smart contracts, and the P-Chain to manage validators and subnets. Additionally, Avalanche's architecture enables fast and cost-effective cross-chain swaps.
Closing Thoughts
The potential of Layer 0 blockchains to tackle challenges like interoperability and scalability in the industry is yet to be determined. Several different solutions are vying for similar objectives, so it will be interesting to observe what kind of impact Layer 0 blockchains make.
Stay tuned to CoinCarp Social Media and Discuss with Us:
Up to $6,045 Bonuses
Sponsored
Join Bybit and receive up to $6,045 in Bonuses! Register Now!